
中国稻米 ›› 2024, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 39-46.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8082.2024.01.007
何旎清1,#, 程朝平1,#, 晋艺丹2, 黄凤凰1, 李生平2, 杨德卫1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-13
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2024-01-23
通讯作者:
*dewei-y@163.com
作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
HE Niqing1,#, CHEN Zhaoping1,#, JIN Yidan2, HUANG Fenghuang1, LI Shengping2, YANG Dewei1,*( )
)
Received:2023-08-13
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2024-01-23
Contact:
*dewei-y@163.com
About author:#Co-first author
摘要:
稻曲病已成为我国水稻生产中重要病害之一,不仅影响水稻产量和品质,且危害人畜健康安全。目前对稻曲病研究已取得一定进展,但在抗性评价标准、抗性基因挖掘、病原菌侵染方式、致病机理以及防控预测等方面还存在局限性。本文综述了稻曲病简史与发生概况、稻曲病菌的生物学特征、稻曲病菌的侵染特征、稻曲病抗性遗传规律与基因鉴定、抗性遗传机制、抗性鉴定技术以及病害发生影响因子等方面的研究进展。同时,探讨当前稻曲病抗性鉴定方法、抗性基因挖掘、侵染机制、稻曲病菌与水稻互作以及病情监测预报和防治等方面存在的问题,分析与展望了相关问题及研究方向。
中图分类号:
何旎清, 程朝平, 晋艺丹, 黄凤凰, 李生平, 杨德卫. 稻曲病发病规律、病菌功能基因组以及免疫反应的遗传机制[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 39-46.
HE Niqing, CHEN Zhaoping, JIN Yidan, HUANG Fenghuang, LI Shengping, YANG Dewei. Pathogenesis and Functional Genomics of Rice False Smut Ustilaginoidea virens and Genetic Mechanism of Immune Response in Rice[J]. China Rice, 2024, 30(1): 39-46.
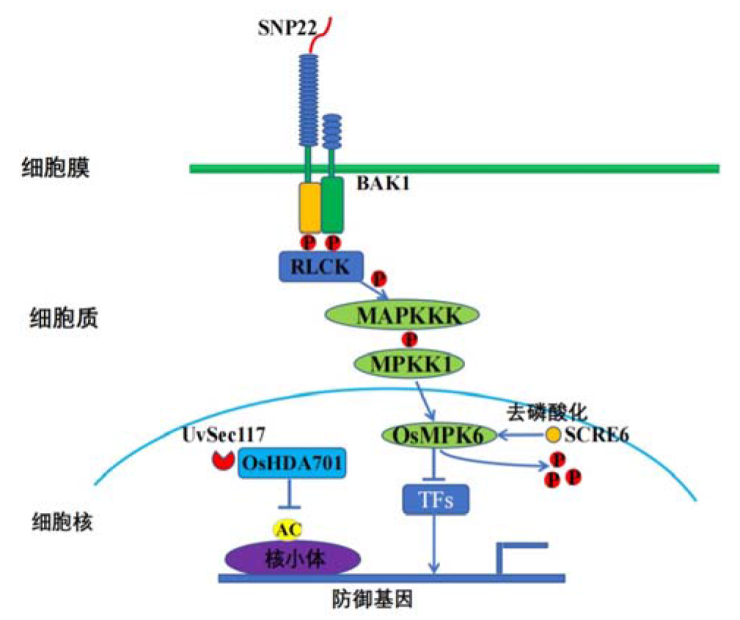
图1 稻曲病菌PAMP触发宿主免疫反应的模型 I,水稻中某些富亮氨酸重复类蛋白激酶与水稻油菜素类固醇受体类激酶BAK1组成的PRR模式识别受体通过识别稻曲菌效应蛋白SNP22,从而激活下游的防御反应;II,稻曲菌中磷酸酶效应因子SCRE6转移到细胞后,与丝裂原活化蛋白激酶6(OsMPK6)相互作用后,使得OsMPK6去磷酸化并增强其稳定性,从而负调控水稻免疫反应;III,稻曲菌中毒性蛋白UvSec117与OsHDA701互作,并将大量的OsHDA701招募到细胞核,进而增强OsHDA701去乙酰化活性,抑制染色体打开,从而抑制转录相关蛋白的结合,进而干扰防御基因的激活和寄主免疫反应。
| [1] | NEELAM K, KUMAR K, KAUR A, et al. High-resolution mapping of the quantitative trait locus (QTLs) conferring resistance to false smut disease in rice[J]. Journal of Applied Genetics, 2022, 63(1): 35-45. |
| [2] | FAN J, YANG J, WANG Y Q, et al. Current understanding on Villosiclava virens, a unique flower-infecting fungus causing rice false smut disease[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2016, 17: 1 321-1 330. |
| [3] | VAN DINGENEN J. A virulence effector resolved: How a fungal phosphatase effector promotes rice false smut[J]. Plant Cell, 2022, 30: 34(8): 2 831-2 832. |
| [4] | RUSH M C, SHAHJAHAN A K M, JONES J P, et al. Outbreak of False Smut of rice in Louisiana[J]. Plant Disease, 2000, 84(1): 100. |
| [5] | FANG A F, GAO H, ZHANG N, et al. A novel effector gene SCRE2 contributes to full virulence of Ustilaginoidea virens to rice[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 845. |
| [6] | 王疏, 白元俊, 刘晓舟, 等. 稻曲病菌白化菌株研究初报[J]. 辽宁农业科学, 1996(6): 45-47. |
| [7] | LI G B, FAN J, WU J L, et al. The flower-infecting fungus Ustilaginoidea virens subverts plant immunity by secreting a chitin-binding protein[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 733 245. |
| [8] | SUN W, FAN J, FANG A, et al. Ustilaginoidea virens: Insights into an emerging rice pathogen[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2020, 58: 363-385. |
| [9] | QIU J H, MENG S, DENG Y Z, et al. Ustilaginoidea virens: A fungus infects rice flower and threats world rice production[J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(4): 199-206. |
| [10] | TANAKA E, ASHIZAWA T, SONODA R, et al. Villosiclava virens gen. nov., comb. nov., teleomorph of Ustilaginoidea virens, the causal agent of rice false smut[J]. Mycotaxon, 2008, 106(1): 491-501. |
| [11] | WANG Y F, WANG F, XIE S L, et al. Development of rice conidiation media for Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. PLoS One. 2019, 24: 14(10): e0217667. |
| [12] | FANG A, FU Z, WANG Z, et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of the rice false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in the Sichuan-Chongqing region[J]. Plant Disease, 2022, 106(1): 93-100. |
| [13] | USMAN M. An overview of our current understanding of diabetic macular ischemia[J]. Cureus, 2018, 10(7): e3064. |
| [14] | TAN Z, BAI Z X, QIN Y B, et al. Characterization of genetic diversity and variation in pathogenicity of the rice false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens from a single source[J]. Plant Disease, 2022, 8: PDIS11212546RE. |
| [15] | PRAMESH D, PRASANNAKUMAR M K, MUNIRAJU K M, et al. Comparative genomics of rice false smut fungi Ustilaginoidea virens Uv-Gvt strain from India reveals genetic diversity and phylogenetic divergence[J]. 3 Biotech, 2020, 10(8): 342. |
| [16] | FU R T, DING L, ZHU J, et al. Morphological structure of propagules and electrophoretic karyotype analysis of false smut Villosiclava virens in rice[J]. The Journal of Microbiology, 2012, 50: 263-269. |
| [17] | WANG X, LIU Q, WANG H, et al. BAC based physical map and genome survey of the rice false smut fungus Villosiclava virens[J]. BMC Genomics, 2013, 14: 883. |
| [18] | SUN X Y, KANG S, ZHANG Y J, et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of rice pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in China[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9): e76879. |
| [19] | ZHANG Y, ZHANG K, FANG A F, et al. Specific adaptation of Ustilaginoidea virens in occupying host florets revealed by comparative and functional genomics[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 3 849. |
| [20] | CHEN X, HAI D, TANG J, et al. UvCom1 is an important regulator required for development and infection in the rice false smut fungus Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Phytopathology, 2020, 110(2): 483-493. |
| [21] | CHEN X, PEI Z, LI P, et al. Quantitative proteomics analysis reveals the function of the putative ester cyclase UvEC1 in the pathogenicity of the rice false smut fungus Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(8): 4 069. |
| [22] | TANG J T, BAI J, CHEN X Y, et al. Two protein kinases UvPmk1 and UvCDC2 with significant functions in conidiation, stress response and pathogenicity of rice false smut fungus Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Current Genetics, 2020, 66(2): 409-420. |
| [23] | CHEN X Y, LI P P, LIU H, et al. A novel transcription factor UvCGBP1 regulates development and virulence of rice false smut fungus Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Virulence, 2021, 12(1): 1 563-1 579. |
| [24] | XIE S L, WANG Y F, WEI W, et al. The bax inhibitor UvBI-1, a negative regulator of mycelial growth and conidiation, mediates stress response and is critical for pathogenicity of the rice false smut fungus Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Current Genetics, 2019, 65(5): 1 185-1 197. |
| [25] | FANG A F, HAN Y Q, ZHANG N, et al. Identification and characterization of plant cell death-inducing secreted proteins from Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Molecular Plant-microbe Interactions, 2016, 29(5): 405-416. |
| [26] | ZHENG M T, DING H, HUANG L, et al. Low-affinity iron transport protein Uvt3277 is important for pathogenesis in the rice false smut fungus Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Current Genetics, 2017, 63: 131-144. |
| [27] | YIN W X, CUI P, WEI W, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor gene family in Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Genome, 2017, 60: 1 051-1 059. |
| [28] | NAKAMURA K I, IZUMIYAMA N, OHTSUBO K I, et al. “Lupinosis”-Like lesions in mice caused by ustiloxin, produced by Ustilaginoidea virens: A morphological study[J]. Natural Toxins, 1994, 2(1): 22-28. |
| [29] | ZHANG K, ZHAO Z, ZHANG Z, et al. Insights into genomic evolution from the chromosomal and mitochondrial genomes of Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Phytopathology Research, 2021, 3: 9. |
| [30] | SUN Q, LIU H, ZHANG Y, et al. Global distribution of ustiloxins in rice and their male-biased hepatotoxicity[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 301: 118 992. |
| [31] | SUN Q, QIAN Z, LIU H, et al. Occurrence and translocation of ustiloxins in rice false smut-occurred paddy fields, Hubei, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 307: 119 460. |
| [32] | IKEGAMI H. Study on the false smut of rice V. Seedling inoculation with the chlamydospores of the false smut fungus[J]. Annals of the Phytopathological Society of Japan, 1962, 27(1): 16-23. |
| [33] | ASHIZAWA T, TAKAHASHI M, ARAI M, et al. Rice false smut pathogen, Ustilaginoidea virens, invades through small gap at the apex of a rice spikelet before heading[J]. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 2012, 78: 255-259. |
| [34] | TEBEEST D O. Infection of rice by Ustilaginoidea virens[J]. Phytopathology, 2010, 100(6): S125. |
| [35] | SONG J H, WANG Y F, YIN W X, et al. Effect of chemical seed treatment on rice false smut control in field[J]. Plant Disease, 2021, 105(10): 3 218-3 223. |
| [36] | TANG X Y, JIN J, HU D W, et al. Elucidation of the infection process of Ustilaginoidea virens (teleomorph: Ustilaginoidea virens) in rice spikelets[J]. Plant Pathology, 2012, 62(1): 1-8. |
| [37] | HU M L, LUO L X, WANG S, et al. Infection processes of Ustilaginoidea virens during artificial inoculation of rice panicles[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2014, 139: 67-77. |
| [38] | SONG J, WEI W, LV B, et al. Rice false smut fungus hijacks the rice nutrients supply by blocking and mimicking the fertilization of rice ovary[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2016, 18(11): 3 840-3 849. |
| [39] | FAN J, LIU J, GONG Z Y, et al. The false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens requires rice stamens for false smut ball formation[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 22(2): 646-659. |
| [40] | SUN Z B, QI J H, SHEN Y, et al. Collection, nucleic acid release, amplification, and visualization platform for rapid field detection of rice false smut[J]. Lab On A Chip, 2023, 23(3): 542-552. |
| [41] | LI Y S, HUANG S D, YANG J, et al. Analysis of quantitative trait loci for resistance to rice false smut[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37: 778-783. |
| [42] | 方先文, 汤陵华, 王艳平. 水稻稻曲病抗性遗传机制[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2008, 24(6): 762-765. |
| [43] | 钱可峰. 水稻稻曲病抗性遗传分析及普遍率与严重度的关系研究[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2012. |
| [44] | 徐建龙, 薛庆中, 罗利军, 等. 近等基因导入系定位水稻抗稻曲病数量性状位点的研究初报[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2002, 14(1): 14-19. |
| [45] | 袁丽华, 黎明, 李军华. 基于一因多效的遗传算法研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2007, 29(11): 1 969-1 972. |
| [46] | ZHOU Y L, XIE X W, ZHANG F, et al. Detection of quantitative resistance loci associated with resistance to rice false smut (Ustilaginoidea virens) using introgression lines[J]. Plant Pathology, 2014, 63: 365-372. |
| [47] | QIU J H, LU F F, WANG H, et al. A candidate gene for the determination of rice resistant to rice false smut[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2020, 40: 105. |
| [48] | LONG W X, YUAN Z Q, FAN F F, et al. Genome-wide association analysis of resistance to rice false smut[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2020, 40: 46. |
| [49] | NEELAM K, KUMAR K, KAUR A, et al. High-resolution mapping of the quantitative trait locus (QTLs) conferring resistance to false smut disease in rice[J]. Journal of Applied Genetics, 2022, 63(1): 35-45. |
| [50] | HUANG Y F, CUI K X, ZHANG Z, et al. Identification and fine-mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTL) conferring rice false smut resistance in rice[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2023, 50(4): 276-279. |
| [51] | LEE D H, LAL N K, LIN Z D, et al. Regulation of reactive oxygen species during plant immunity through phosphorylation and ubiquitination of RBOHD[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 1 838. |
| [52] | SONG T Q, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Q, et al. The N-terminus of an Ustilaginoidea virens Ser- Thr- rich glycosylphosphatidylinositol- anchored protein elicits plant immunity as a MAMP[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 2451. |
| [53] | ZHENG X H, FANG A F, QIU S S, et al. Ustilaginoidea virens secretes a family of phosphatases that stabilize the negative immune regulator OsMPK6 and suppress plant immunity[J]. The Plant Cell, 2022, 34(8): 3 088-3 109. |
| [54] | CHEN X Y, DUAN Y H, QIAO F G, et al. A secreted fungal effector suppresses rice immunity through host histone hypoacetylation[J]. New Phytologist, 2022, 235(5): 1 977-1 994. |
| [55] | 胡建坤, 黄蓉, 李湘民, 等. 东乡野生稻对稻曲病抗性鉴定与分析[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2021, 43(4): 774-782. |
| [56] | 王连平, 董明灶, 郝中娜, 等. 浙江省水稻品种抗稻曲病自然诱发鉴定初步研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 2010, 22(7): 73-74. |
| [57] | 缪巧明, 王永华. 水稻品种对稻曲病的抗病性鉴定技术研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 1994, 7(2): 67-70. |
| [58] | 黄金杯, 刘二明, 肖启明, 等. 18个水稻品种抗稻曲病的田间抗性评价[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2009(1): 69-72. |
| [59] | IRRI. Standard evaluation system for rice[M]. Manila: International Rice Research Institute, 1980. |
| [60] | 陈嘉孚, 邓根生, 杨治华, 等. 稻种资源对稻曲病抗性鉴定研究[J]. 作物品种资源, 1992(2): 35-36. |
| [61] | 何会流, 毛建辉, 卢代华, 等. 四川水稻品种对稻瘟病和稻曲病抗性评价[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 30(7): 104-109. |
| [62] | 唐春生, 高家樟, 曹国平, 等. 稻曲病病情分级标准的研究和应用[J]. 植物保护, 2001, 27(1): 18-21. |
| [63] | 施辰子, 郭玉人, 陆保理, 等. 水稻稻曲病分级标准及导致产量损失的初步测定[J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 2003, 21(2): 152-155. |
| [64] | 李小娟, 刘二明, 肖启明, 等. 水稻对稻曲病抗性的分级及相应级别的产量损失[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 37(3): 275-279. |
| [65] | 吴格娥, 魏永建, 刘琳丰, 等. 影响稻曲病发生的几个因素分析[J]. 耕作与栽培, 2000(6): 60-61. |
| [66] | 王文斌, 尹小乐, 李燕, 等. 影响稻曲病严重度主要因素的研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2014, 27(3): 1 067-1 071. |
| [67] | TANAKA S, BREFORT T, NEIDIG N, et al. A secreted Ustilago maydis effector promotes virulence by targeting anthocyanin biosynthesis in maize[J]. Elife, 2014, 3: e1355. |
| [68] | 眭立仁, 宋志龙. 稻曲病病因观察调查和思考[J]. 上海农业科技, 2005(4): 100-101. |
| [69] | 岑汤校, 张震, 张昌杰, 等. 氮磷钾施肥水平对水稻稻曲病为害的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2014(2): 225-226. |
| [70] | WANG A J, ZHA Z P, YIN D S, et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis of Tilletia horrida infection in resistant and susceptible rice (Oryza sativa L.) male sterile lines reveals potential candidate genes and resistance mechanisms[J]. Genomics, 2020, 112(6): 5 214-5 226. |
| [71] | 张正炜, 陈秀, 沈慧梅, 等. 我国稻曲病分级标准的研究与应用现状[J]. 中国稻米, 2020, 26(4): 18-21. |
| [72] | 徐伟东, 李冠, 陆强, 等. 水稻稻曲病研究现状及展望[J]. 作物研究, 2018, 32(1): 76-81. |
| [73] | 张俊喜, 成晓松, 宋益民, 等. 中国水稻稻曲病研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2016, 32(1): 234-240. |
| [1] | 喻梓轩, 刘新勇, 张健, 梁大成. 生长素调控水稻生长发育的研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 1-9. |
| [2] | 马瑗蕊, 石艳平, 黄其颖, 任佳佳, 郭俏俏, 徐彦, 徐炜杰, 柳丹. 水肥和钝化剂阻控水稻吸收镉机制的研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 10-17. |
| [3] | 王振洋, 王冀川, 袁杰, 王奉斌. 不同肥密措施对南疆水稻抗倒伏及干物质生产特性和产量的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 101-107. |
| [4] | 毛名义, 杨文荟, 管艳伟, 潘宗东, 周丽洁, 余显权. 基于表型性状构建禾初级核心种质[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 18-25. |
| [5] | 陈云, 孟轶, 翁文安, 陈雨琼, 张洪程, 廖萍. 硝化抑制剂双氰胺施用对水稻产量和温室气体排放的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 26-29. |
| [6] | 薛颖昊, 孙国峰, 眭鑫梅, 陈旭蕾, 孙仁华, 徐志宇. 不同腐熟剂对麦秸腐解率与稻田水环境的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 30-35. |
| [7] | 董振杰, 陆尧, 李京咏, 窦志, 张洪程, 高辉. 稻田综合种养土壤重金属空间变异特征与质量安全评价研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 36-38. |
| [8] | 梁文豪, 胡时开, 圣忠华, 魏祥进, 焦桂爱, 邵高能, 谢黎虹, 王玲, 唐绍清, 胡培松. 外源氨基酸对层出镰刀菌菌丝生长和伏马毒素合成的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 47-52. |
| [9] | 冯春炜, 王晓林, 郭庆林, 张琰, 姚丽娜, 金茜雯, 符致昊, 黄玉韬, 曹栋栋, 朱叶峰. 机械干燥对水稻种子质量影响的研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 53-57. |
| [10] | 高义卓, 向镜, 叶天承, 孙凯旋, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 张义凯, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 张运波. 不同光质配比的LED光源补光对水稻机插秧苗生长发育的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 58-62. |
| [11] | 林芗华. 稻谷对铅富集特性的品种差异及其安全风险[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 63-68. |
| [12] | 张容慧, 张秀锦, 柴冠群, 范成五, 何腾兵, 秦松. 贵州青黄泥田重金属元素低积累水稻品种筛选[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 75-83. |
| [13] | 邹旭东, 李荣平, 曹士民, 蔡福, 米娜, 王笑影. 盘锦水稻田碳通量变化特征研究[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 84-92. |
| [14] | 童纪氚, 戎雪利, 任萍, 褚光, 王丹英. 水稻无人机直播产量、效益分析及技术要点[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(1): 98-100. |
| [15] | 占小登, 王凯, 曹立勇. 近年我国水稻遗传育种研究进展与展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(6): 1-4. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||